We usually focus on nutrition during pregnancy and breastfeeding, however, adequate nutrients during preconception is just as important for a healthy pregnancy and optimal development of your baby.
When preparing to conceive, it is usually recommended that you take specific supplements and have a well-balanced diet rich in lean protein, healthy fats, vegetables, fruits and high fibre staples.
It is recommended that you make these healthy lifestyle changes at least three months to a year before you conceive.
What to eat if you're trying to get pregnant
When planning meals, you should consider these specific nutrients and foods that are essential for preconception:
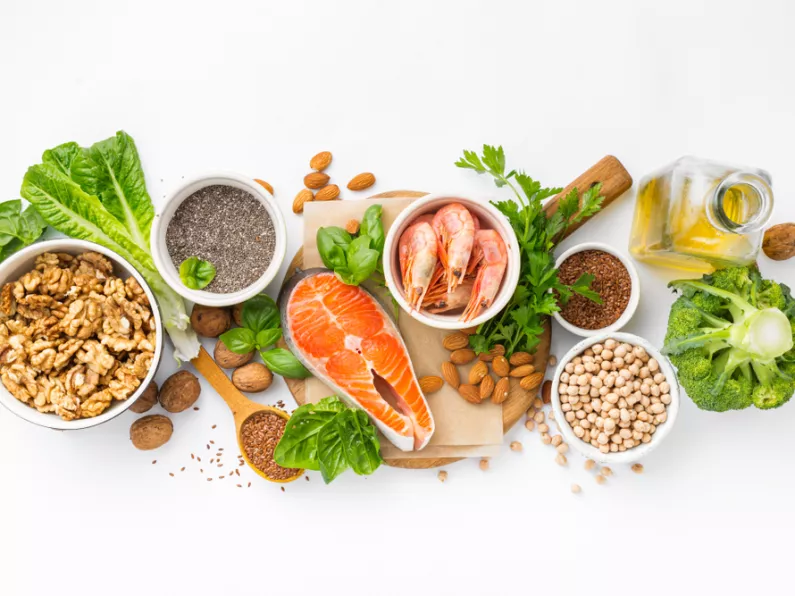
- Folate and Folic Acid: This is important for the formation of the baby's neural tube that develops into the brain and spinal cord. Adequate folic acid intake before conception and during early pregnancy can reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Foods rich in folate include leafy greens (spinach, lettuce, broccoli etc.), citrus fruits, peas, beans, seeds, nuts and whole grain cereals fortified with folic acid.
- Iron: Blood volume increases during pregnancy and iron is an essential nutrient for the production of red blood cells, as well as to transport oxygen throughout the body. As such, it is wise to build your body’s iron stores with iron-rich foods before getting pregnant. These foods include liver, meats, seafood, peas, beans, seeds, nuts, dried fruit and green leafy vegetables. Remember to combine these foods with vitamin C-rich sources such as citrus fruits, sweet peppers, tomatoes, West Indian cherries, guava, pawpaw and mangoes, to enhance iron absorption.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: To support the development of healthy eyes and brain of your baby, omega-3 fatty acids should be consumed daily. These healthy fats can be found in fatty fish like salmon and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Calcium: For strong bones and teeth in both the mother and the growing baby, consume calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, calcium fortified plant-based milks and food products.
- Vitamin D: The sunshine vitamin is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. You can boost your vitamin D levels by exposure to sunlight, but don’t forget to wear sunscreen! Calcium food sources include sardines and other fatty fish, egg yolks and fortified dairy or plant-based milks.
- Iodine: Healthy thyroid function for hormonal balance and a baby's cognitive development require adequate iodine. Rich sources of iodine include, seafood, sea moss, dairy products and iodized salt.
Supplementation
It is not advised to get a supplement for each nutrient discussed, as excessive supplementation can actually be harmful to your health.
Rather, you should consult with your Dietitian to assess your nutritional needs, as it may vary for each woman.
In general, to support your conception journey, focus on consuming a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated, limiting processed foods, and avoiding alcohol and excessive caffeine.