A food allergy is an abnormal response of the body's immune system to certain foods.
This is not the same as food intolerance, although some of the symptoms may be very similar.
When your body fights what it senses as danger, this can cause allergy symptoms like hives, asthma, wheezing, trouble breathing, stomach pains, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Which foods can cause allergic reactions in babies?
About 90% of food allergies are caused by:
- Milk
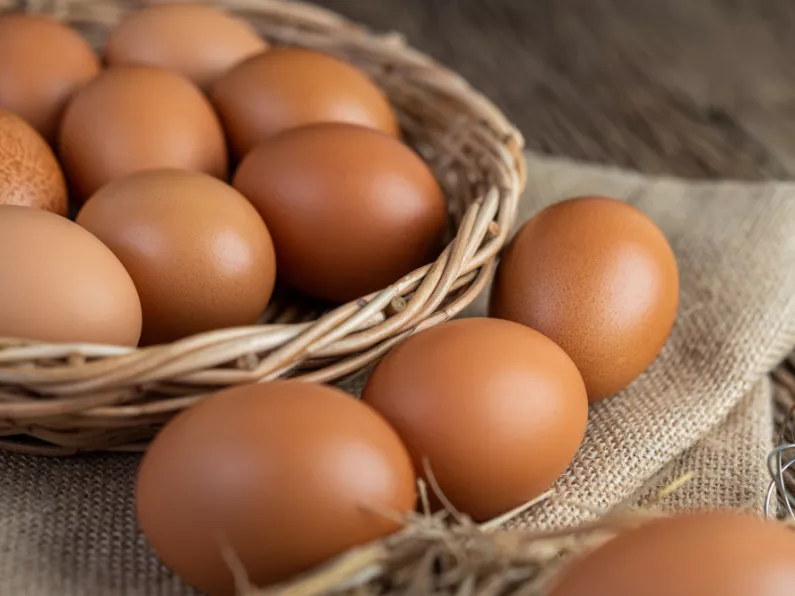
- Eggs
- Wheat
- Soy
- Tree nuts
- Fish
- Shellfish
- Peanuts
Food allergy facts
- Eggs, milk, and peanuts are the most common causes of food allergies in children
- Peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish commonly cause the most severe reactions
- Nearly 1 in 20 children under the age of 5 have food allergies
- Most children outgrow their allergies. But allergies to peanuts, tree nuts, and shellfish may be lifelong.
Introducing foods that are likely to trigger an allergy
Every baby is different, but some foods are more likely to trigger an allergic reaction.
This doesn't mean these foods need to be avoided completely. It’s fine to introduce these foods from around six months, but it’s best to introduce them one at a time and in small amounts to start with.
That way you will recognise which ones trigger allergies so you can cut them out going forward.
Family history
Your little one is more likely to develop an allergy if you have a family history of asthma, eczema, hay fever or a particular food allergy.
If any of these apply, speak to your pediatrician before you start weaning your baby.
How to reduce the risk of your baby developing allergies
Breastfeeding is the best protection you can offer your baby against allergies.
Treatment for food allergy
There is no medication to prevent food allergy so it's vital to avoid the foods that cause the symptoms.
If you are breastfeeding your child, it is important to avoid these foods in your diet.
For children who have had severe food reactions, your pediatrician may prescribe an emergency kit to deal with severe symptoms.